Nowadays, you’re likely to find USB Type C on various devices, from your smartphone to your laptop. But have you ever stopped to think about what makes it so special and how it differs from other connectors we’ve used for years? When you discover the details behind this connector, you realize it’s not just a technological evolution; it’s a significant shift in how we interact with our devices.

What is USB Type C and How Does It Differ From Other Connectors?
USB Type C is a type of connector that has gained popularity in recent years, mainly due to its small size and reversible design. This means that no matter how you plug it in, it will always connect the right way, eliminating the frustration of trying to plug something in upside down. But beyond this convenience, USB Type C is much more than just a connector.
| Feature | USB Type C | Other USB Connectors |
|---|---|---|
| Size | Small | Varies (Type A large, Type B medium) |
| Reversibility | Yes | No |
| Transfer Speed | Up to 40 Gbps with Thunderbolt 3 | Varies (up to 5 Gbps with USB 3.0) |
USB Type C does not determine transfer speed or the technology that can be used by itself. This depends on the standard or protocol it supports, such as USB 3.1, one of the most recent and fastest, or even Thunderbolt 3, which takes transfer speeds to impressive levels. In other words, the Type C connector is just the tip of the iceberg; the real interest lies in what’s behind this small port.
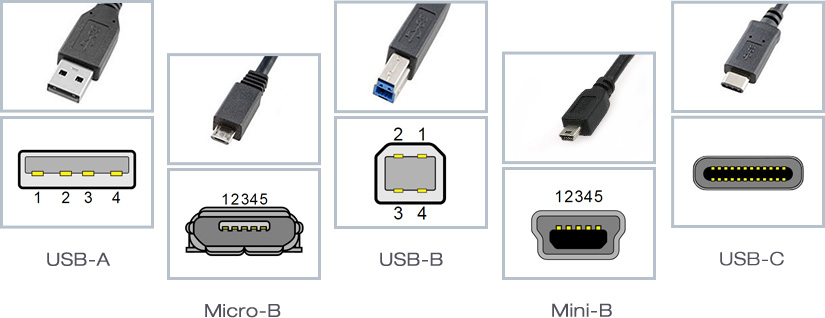
Classes of USB: How Do They Compare to USB Type C?
There are several types of USB connectors, each with its own characteristics and limitations. Here’s a brief overview of the most common types and why USB Type C is superior:
- USB Type A:
- Size: Large and rectangular.
- Reversibility: No, it can only connect in one direction.
- Speed: Up to 5 Gbps with USB 3.0.
- Common Use: Devices like keyboards, mice, and external hard drives.
- Limitation: Its size and lack of reversibility make it less convenient compared to Type C.
- USB Type B:
- Size: Medium, generally square.
- Reversibility: No, it can only connect in one direction.
- Speed: Varies depending on the standard, but typically slower than Type C.
- Common Use: Printers and scanners.
- Limitation: Less common in modern devices, larger size.
- MicroUSB:
- Size: Small.
- Reversibility: No, it can only connect in one direction.
- Speed: Up to 480 Mbps with USB 2.0.
- Common Use: Older smartphones and small devices.
- Limitation: Limited speed and lack of reversibility.
- MiniUSB:
- Size: Slightly larger than MicroUSB.
- Reversibility: No, it can only connect in one direction.
- Speed: Up to 480 Mbps with USB 2.0.
- Common Use: Older digital cameras and some mobile devices.
- Limitation: Obsolete in most current devices.
- USB Type C:
- Size: Small and oval.
- Reversibility: Yes, it can connect in any direction.
- Speed: Up to 40 Gbps with Thunderbolt 3.
- Common Use: Smartphones, laptops, tablets, and more.
- Advantage: Modern design, high speed, versatile in power supply and data transmission, and compatibility with multiple technologies.
As you can see, USB Type C not only offers greater speed and functionality compared to other USB types but also solves common problems such as the lack of reversibility and the need for multiple types of connectors.
What is USB Type C Used For and How to Maximize Its Capabilities
USB Type C is extremely versatile. It can be used not only to transfer data at high speeds but also to charge devices with significant power thanks to USB Power Delivery (USB PD). This power supply capability is so powerful that some manufacturers are starting to phase out proprietary chargers in favor of this connector, which can power everything from a smartphone to a laptop.
| USB Type C Use | Description |
|---|---|
| Data Transfer | Supports USB 3.1 and Thunderbolt 3 for ultra-fast speeds |
| Power Supply | USB Power Delivery allows charging large and small devices |
| Video and Audio Output | Compatible with HDMI, DisplayPort, and more |
USB Type C’s compatibility with various technologies, such as HDMI or DisplayPort, makes it a unique choice for those looking for an all-in-one connector. However, this is also where confusion arises. Not all Type C cables or ports are the same, and not all support the same technologies, leaving users wondering if they’re making the most of their equipment.

How Does USB Type C Really Differ From Other Connectors?
At first glance, USB Type C stands out for its oval and symmetrical head, something not seen in other connectors like USB Type A or MicroUSB. Beyond its design, the most important differences lie in the technologies it can support. While other connectors are limited to older protocols, Type C is designed for the most advanced standards, ensuring higher speed and capacity.
| Technology | USB Type C | Other USB Connectors |
|---|---|---|
| Thunderbolt 3 | Yes | No |
| USB 3.1 | Yes | Limited to some connectors |
| Reversibility | Yes | No |
When you look at transfer speeds, USB Type C using USB 3.1 or Thunderbolt 3 can reach speeds that other connectors simply cannot match. This makes it the ideal choice for those seeking efficiency and performance in their devices.
User Opinions and the MundoVirtual Perspective
At MundoVirtual, we’ve seen how USB Type C has revolutionized the way we use our devices. The adoption of this connector has not only simplified our connections but also driven greater interoperability between different devices and brands. Users highlight its versatility but also express some frustration due to the lack of clear standardization by manufacturers. As more devices adopt USB Type C, we hope to see greater clarity and uniformity in its implementation.
“Keep watching on MundoVirtual”
- iPhone 17 Pro Max: el golpe sobre la mesa que no te esperabas

- No te compres nada todavía: el iPhone 17 Pro me hizo replantearlo todo”

- “No lo vas a soltar”: el teléfono ultrafino que me hizo replantear qué espero de un iPhone

- No compres otro teléfono hasta leer esto: el salto silencioso que cambia las reglas

- Se acabó quedarse incomunicado: así llega el Apple Watch Ultra 3

- Tu muñeca se volvió pro: el Apple Watch Series 11 cambia las reglas y te cuento por qué

And you, have you already experienced the advantages of USB Type C? What do you think about its implementation in current devices? Join the conversation, and don’t forget to subscribe to our social networks and MundoVirtual to stay updated on all the technological news that’s coming. We look forward to your comments!




